When it comes to gardening and growing plants, there are few things as important as soil health and plant nutrition. As someone who has always been passionate about gardening and understanding the intricacies of plant growth, I have spent countless hours researching and experimenting with different soil types and fertilizers. In this blog post, I want to share with you the basics of soil health and plant nutrition, combining my personal experiences with the knowledge I have gained over the years.
To start off, let’s talk about soil health. Healthy soil is the foundation for vibrant and thriving plants. It not only provides essential nutrients but also maintains proper moisture levels, allows for good drainage, and promotes beneficial microbial activity. When your soil is healthy, your plants are more resistant to diseases and pests, and they have stronger root systems, allowing them to better absorb nutrients.
One of the key factors in soil health is the composition of the soil. There are three main components: sand, silt, and clay. The ideal soil composition is loam, which is a balanced mixture of all three components. Loam soil has good drainage and retains moisture well. If your soil is sandy, it drains too quickly, and if it’s clayey, it retains too much water, leading to potential root rot. Depending on your soil type, you may need to amend it to achieve a more balanced composition.
Another important aspect of soil health is the pH level. pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, and it affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, around 6 to 7. If your soil is too acidic, you can add lime to raise the pH, and if it’s too alkaline, you can add sulfur or peat moss to lower it. Testing your soil’s pH is easy with the help of a home testing kit, which you can find at most garden centers or online.
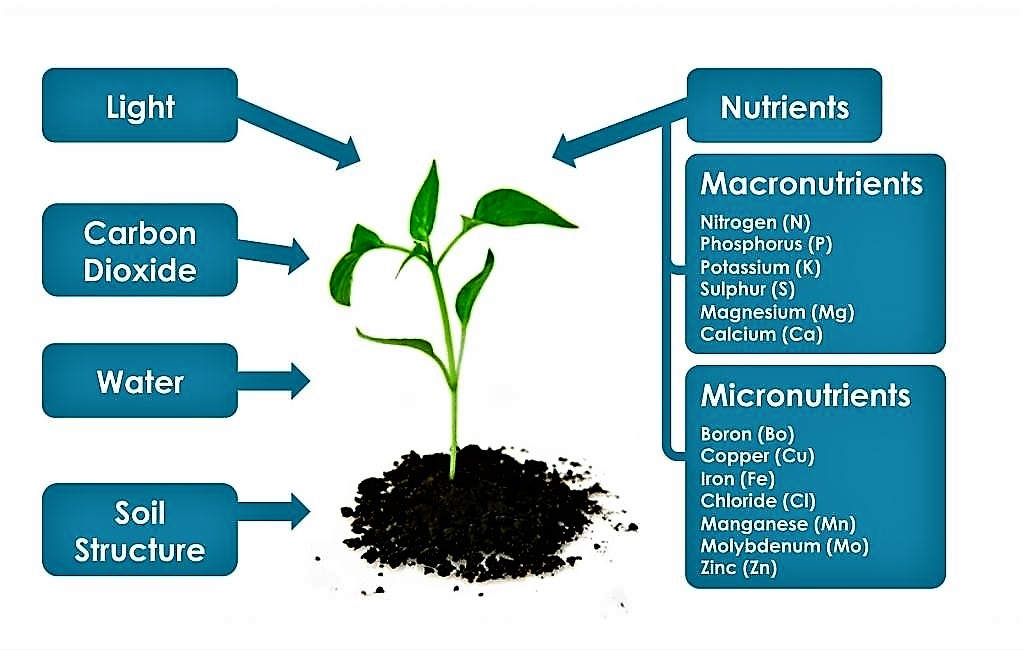
Now that we have covered the basics of soil health, let’s move on to plant nutrition. Like humans, plants require a balanced diet to grow and thrive. Just as we need carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, plants need macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients are the primary nutrients that plants require in large quantities. They include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), often referred to as NPK. Nitrogen promotes leaf and stem growth, phosphorus aids in root development and flowering, and potassium improves overall plant health and resistance to diseases.
Micronutrients, on the other hand, are required in much smaller amounts but are equally essential. They include elements like iron, manganese, zinc, copper, and others. Micronutrients help with various processes in plants, such as photosynthesis, enzyme activation, and nutrient absorption.
To ensure your plants receive the proper nutrition, it’s essential to fertilize your soil. There are two main types of fertilizers: organic and synthetic. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as compost, manure, bone meal, and fish emulsion. They release nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply of nutrition to the plants over time. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are manufactured through chemical processes. They often have higher concentrations of nutrients and provide an immediate boost to plants. Both types have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on your personal preferences and gardening goals.
In addition to fertilizers, organic matter plays a crucial role in plant nutrition. Adding organic matter to your soil helps improve its structure, drainage, and nutrient-holding capacity. It also feeds beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and bacteria, which in turn enhance nutrient cycling and soil health. Organic matter can be in the form of compost, leaf mold, or well-rotted manure. Adding a layer of organic mulch on top of your soil also helps conserve moisture and suppress weed growth.
I have seen firsthand the incredible impact that good soil health and proper plant nutrition can have on the growth and vitality of plants. When I started paying closer attention to these aspects, my garden transformed into a lush and thriving paradise. It took time and experimentation to find the right balance for my specific plants, but the rewards were well worth it.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of soil health and plant nutrition is crucial for any gardener or plant enthusiast. By focusing on the composition and pH of your soil, as well as providing the right combination of macronutrients, micronutrients, and organic matter, you can create an optimal environment for your plants to flourish. So, go ahead and get your hands dirty, experiment with different fertilizers, and watch your garden come to life with vibrancy and abundance. Happy gardening!